What do we mean by ESRS – European Sustainability Reporting Standards?
ESRS – European Sustainability Reporting Standards – is a set of standards that translate CSRD requirements into practice. In the article, we summarise their main features in a few points for those who are learning about the new sustainability reporting requirements.
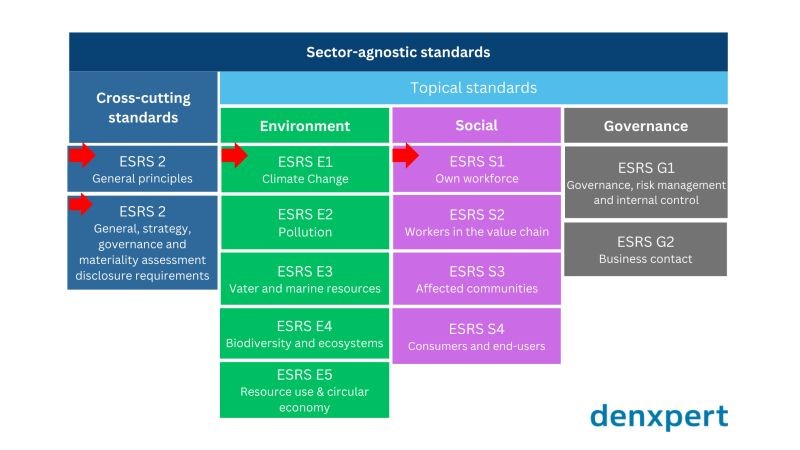
Structure of standards required by the CSRD (Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive)
The CSRD requires large companies to collect and report sustainability information about their activities in accordance with the ESRS standards developed by EFRAG (European Financial Reporting Advisory Group). The set of sector-agnostic standards published by EFRAG so far includes two overarching standards and a total of 10 thematic standards, currently only in proposal form. The thematic standards contain:
- 5 standards on environmental topics,
- 4 standards on social issues
- 1 standard covers corporate governance issues.
ESRS 1, ESRS 2 and ESRS E1 standards
All companies affected by CSRD will be required to comply with the requirements of ESRS 1, ESRS 2 and ESRS E1. In addition, companies with more than 250 employees will also be subject to ESRS S1. What is covered by each standard?
- ESRS 1: general principles
- ESRS 2: general strategy, governance and materiality assessment, disclosure requirements
- ESRS E1: climate change related standard
- ESRS1 S1: own workforce related standard